Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews April 30, 2024 April 23, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Carbohydrates are among the most abundant compounds on earth. They are normally broken down into five major classifications of carbohydrates:
The word monosaccharide is derived from mono, meaning "one", and saccharide,
meaning "sugar". The common monosaccharides are glucose, fructose, and
galactose. Each simple sugar has a cyclic structure and is composed of
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in ratios of 1:2:1 respectively. Although each
sugar mainly exists as a cyclic compound, it is important to note that they are
all in equilibrium to a small extent with their linear forms.
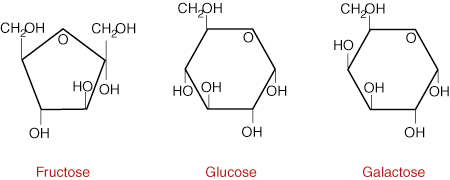
Glucose is the main sugar metabolized by the body for energy. The D-isomer of glucose predominates in nature and it is for this reason that the enzymes in our body have adapted to binding this form only. Since it is an important energy source, the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream usually falls within a narrow range of 70 to 115mg/100 ml of blood. Sources of glucose include starch, the major storage form of carbohydrate in plants.
Galactose is nearly identical to glucose in structure except for one hydroxyl
group on carbon atom number four of the six-sided sugar. Since it differs in
only one position about all six asymmetric centers in the linear form of the
sugar, galactose is known as an epimer of glucose. Galactose is not
normally found in nature in large quantities, however it combines with glucose
to form lactose in milk. After being absorbed by the body, galactose is
converted into glucose by the liver so that it can be used to provide energy for
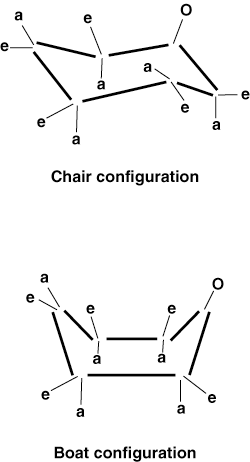
the body. Both galactose and glucose are very stable in solution because they
are able to adopt chair and boat conformations.
Fructose is a structural isomer of glucose, meaning it has the same chemical ormula but a completely different three-dimensional structure. The main difference is that fructose is a ketone in its linear form while glucose is an aldehyde. Through an intramolecular addition reaction with the C-5 OH group, glucose forms a six-membered ring while fructose forms a five-membered ring as seen in Figure 1. Upon consumption, fructose is absorbed and converted into glucose by the liver in the same manner as lactose. Sources of fructose include fruit, honey and high-fructose corn syrup.
Disaccharides, meaning "two sugars", are commonly found in nature as sucrose, lactose and maltose. They are formed by a condensation reaction where one molecule of water condenses or is released during the joining of two monosaccharides. The type of bond that is formed between the two sugars is called a glycosidic bond.
Please wait while we process your payment

