Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews April 30, 2024 April 23, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Coronary heart disease is the most common cause of morbidity and mortality in the developed world. More than 500,000 deaths a year are attributed to coronary heart disease in the US. At least a third of the individuals that die of coronary heart disease are younger than 55 years of age. This disease costs the US over 100 billion dollars per year in medical treatment and lost income.
One of the primary risk factors for heart disease is hyperlipidemia, also prevalent in the US and throughout the developed world. Moreover, as inhabitants of the developing world now begin to have access to more fats in their diets and to lead more sedentary lives, the disease will become an increasing problem there as well. The increased intake of saturated fats and decreased intake of complex carbohydrates and foods high in fiber predispose a person to hyperlipidemia. A sedentary lifestyle contributes to the prevalence and severity of the dysmetabolic syndrome that includes increases in total and LDL cholesterol and also low HDL cholesterol, insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, obesity, and hypertension. These factors contribute to the prevalence and severity of the clinical sequelae of hyperlipidemia, including coronary heart disease.
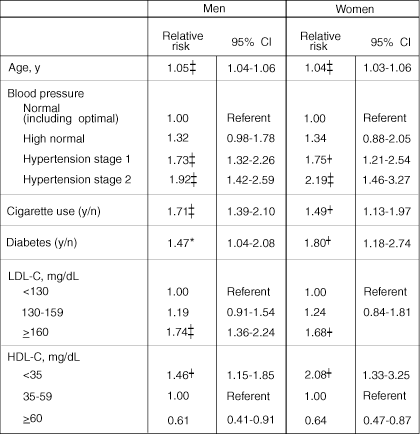
Serum total and LDL cholesterol are continuous predictor variables that confer risk across a broad range (including some values in the 'normal' range). Low HDL cholesterol is associated with an increased risk of coronary heart disease, even in the absence of elevated LDL cholesterol. This absolute risk of disease is modified by the presence or absence of additional cardiovascular risk factors. These risk factors include age, gender, family history, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes mellitus. Hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and smoking are modifiable risk factors. It remains unclear whether diabetes mellitus and low HDL cholesterol are truly modifiable risk factors, although recent evidence suggests that correction of these metabolic abnormalities confers a small reduction in cumulative risk. The cumulative risk resulting from the presence of more than one risk factor is multiplicative and not simply additive.
Please wait while we process your payment

