The several existing forms of vitamin K have similar biological activity in blood clotting. Phylloquinone is the major form found in plants. Menaquinone is synthesized by intestinal bacterial flora. Menadione is a water-soluble vitamin K analog.
Function
Vitamin K functions in the clotting of blood. There are seven vitamin K dependent coagulation proteins, or factors, that are proenzymes. All require calcium for activation. A prothrombinase complex on the platelet membrane converts prothrombin (vitamin K clotting protein) to thrombin, which converts fibrinogen to fibrin. There are two vitamin K dependent bone proteins that serve an unclear role in bone metabolism.
Absorption and excretion
Vitamin K is absorbed into the small intestine and incorporated in chylomicrons. It then enters the lymphatic system and is transported through the body. In the liver, some vitamin K is stored, some is oxidized, and some is re-secreted with very low density lipoprotein (VLDL). Most vitamin K is excreted in the feces. Fat malabsorption syndromes result in decreased vitamin K absorption. Hyperlipidemia decreases the transfer of vitamin K to tissues.
Clinical conditions
Vitamin K deficiency is rare in adults and is more likely to occur in breast-fed newborns. Vitamin K deficiency results in easy bruising and bleeding, such as gastrointestinal hemorrhage, menorrhagia, and hematuria. Newborns are susceptible to vitamin K deficiency because the placenta is a poor transmittor of lipids, the neonatal liver is immature with respect to prothrombin synthesis, breastmilk is low in vitamin K, and the infant gut is sterile in the first few days of life. Vitamin K deficiency in newborns is called Hemorragic Disease of the Newborn.Malabsorption syndromes and other gastrointestinal disorders decrease vitamin K. Liver disease can result in hypoprothrombinemia whereby the liver is unable to use vitamin K to synthesize vitamin K-dependent factors. Drug therapy can result in a vitamin K deficiency. Drugs such as coumarin, salicyclates, some antibiotics, and megadoses of vitamin A and vitamin E antagonize the action of vitamin K.
Recommended intake
Vitamin K requirements can easily be met by the diet and by microbial biosynthesis in the gut. The RDA for vitamin K is 5-10 mcg for infants, 15-30 mcg for children, 45-60 mcg for adolescents, 60-65 mcg for adult women, 70-80 mcg for adult men, and 65 mcg for pregnant and lactating women.
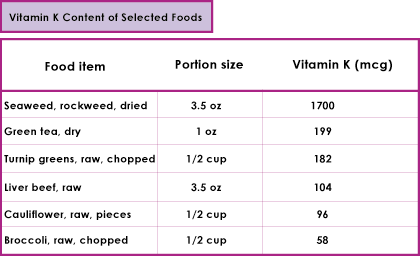
Food Sources
Phylloquinone is widely distributed in plant foods, especially high in green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, turnip greens, and green tea leaves. Menaquinone is found in liver and some cheeses.
Supplementation
To prevent hemorrhagic disease, 1 mg of the phyolloquinone form of vitamin K is injected into newborns at birth. No toxicity has been seen at intakes 500 times the RDA.


 payment page
payment page



