Suggestions
Use up and down arrows to review and enter to select.Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews May 1, 2024 April 24, 2024
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Folic acid, also called folate, is involved in DNA and protein synthesis. It has a role in the synthesis of the amino acid methionine which is involved in lipid metabolism. Folic acid has a primary role in systems involved with the transfer of single carbon units to other substances. Such reactions include: purine synthesis, pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis, and the conversion of three amino acids. These conversions include the interconversion of the nonessential amino acids serine and glycine, the catabolism of histidine to glutamic acid, and the conversion of homocysteine to methionine.
Folic acid is absorbed primarily in the proximal third portion of the small intestine. Folate in food is in the form of polyglutamate. Excess glutamates must be split off to make folate absorbable. Approximately one-half of the stored folate is in the liver. Folate is excreted in the urine and bile.
Folic acid deficiency has six major causes:
The recommendations for folate have doubled from the 1989 RDA to the 1998 DRI due to the importance of folate in preventing neural tube defects. The current daily recommendations are as follows, 65-80 mcg for infants, 150-200 mcg for children, 300-400 mcg for adolescents, 400 mcg for adults, 600 mcg for pregnant women, and 500 mcg for lactating women. The requirements for folate increase with factors that result in an increased metabolic rate, such as infection and hyperthyroidism, and with conditions in which there is a rapid cell turnover, such as the rapid tissue growth of the fetus or malignant tissue. Requirements are also increased with high alcohol intake.
Primary folate sources include yeast, liver, fresh green vegetables, and fresh fruits such as oranges. Folate is a heat-labile substance that is easily destroyed by cooking, especially in water. Up to 50-90% of folate may be destroyed by cooking.
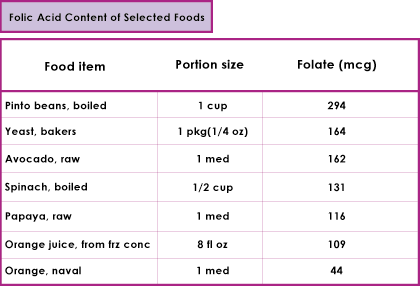
Folate supplementation is primarily used to prevent neural tube defects. The recommendation for fertile women is 400 mcg and increases to 600 mcg during pregnancy. The Food and Drug Administration has mandated the fortification of grain products with folate. Up to 15 mg of folate per day will not cause toxicity. Very high doses may have a convulsant effect, and a dose of 350 mg per day has been reported to cause zinc deficiency.
Please wait while we process your payment

