Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!

Annual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
You could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

SAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Energy, Concentration, and Potential
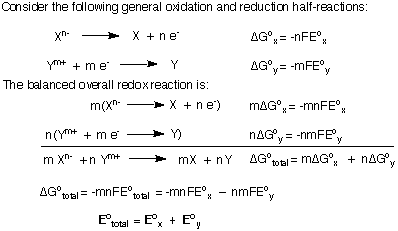
Note that in the that the ΔG's were added together and then we solved for Eototal instead of simply adding the Eo's. As that proof shows, if there are no "left-over" electr ons in the overall balanced equation, then you can sum the potentials of the half-reactions.
However, if you are trying to add two reduction potentials to generate the reduction potential of a new reaction, your balanced equation will have some left-over electrons and you cannot simply add the two reduction potentials together. I will derive the formula for adding reduction or oxidation potentials together to generate a new half-reaction. I will use the reduction of Fe3+ to Fe metal as my example. Be sure to understand the important conclusion that when summing reduction potentials, Eototal does not equal the sum of the individual Eo's.
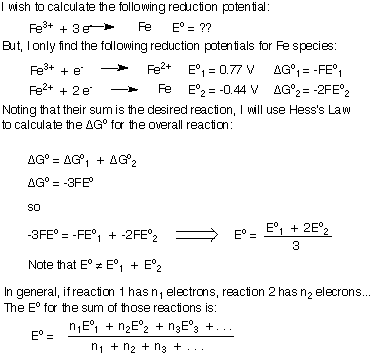
So far in our discussion of electrochemical cells, we have only considered reactions at "standard state" which are, in reality, impossible to achieve. The moment you hook up the wire connecting two half-cells the reaction proceeds and changes the concentrations of all reactants and products. Furthermore, if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic, the reaction mixture will heat or cool making it deviate from the standard temperature. Therefore, we need a way to relate Eo at the standard conditions and E, the potential at any real condition. That relationship, called the Nernst Equation, was first derived by Walther Nernst and earned him the 1920 Nobel Prize in chemistry. The is found below:
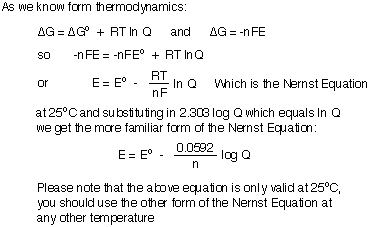
Please note that the familiar form of the Nernst Equation is only applicable when the reaction is carried out at 25oC (298oK). At any other temperature you need to use the first form of the Nernst Equation: E = Eo - (RT/nF) ln Q. One caveat in using the Nernst Equation: Q is the reaction quotient, so you must have already balanced the redox reaction to be able to place the correct power on each concentration term in Q. Make sure you use consistent units for both R and T!
As you can tell by inspection of the Nernst equation the cell potential depends on concentration. In fact, the equation implies directly that you can construct a galvanic cell with half-cells of identical composition but differing concentrations--a concentration cell. As is intuitively obvious from our knowledge of osmotic pressure a concentration cell reacts in such a manner as to dilute the more concentrated half-cell and to concentrate the more dilute half-cell as shown in .
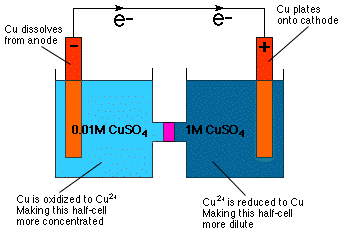
As shown in the , the dilution of the cathode half-cell is achieved by reducing Cu2+ to Cu metal and plating that metal onto the Cu electrode. In the anode half-cell, the Cu anode is oxidized to Cu2+ and, thus, dissolved into the solution, making the anode cell more concentrated.
Please wait while we process your payment





