-
Closed Interval
A set of numbers on the number line that is bounded by two endpoints and that includes the endpoints. For example, the closed interval [- 2, 2] contains all the numbers greater than or equal to -2 and less than or equal to 2. A closed endpoint is denoted by a bracket around the endpoint. Intervals may also be closed at one endpoint and open at the other.
-
Composite Function
A combination of two functions in which the output of one function is the input for the other. The composite of f and g, written as (fog)(x), means f (g(x)).
-
Constant Function
This is a function whose value is always constant and does not vary with the input. For example, f (x) = 4 is a constant function.
-
Continuous
Intuitively, a function is continuous if you can draw it without lifting your pen from the paper. Formally, a function f (x) is continuous at a point x = c if the following is true at that point:
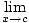 f (x) = f (c)
f (x) = f (c)
A continuous function is one that is continuous for all points in its domain. -
Domain
The domain of a function f is the set of all real numbers for which f is defined.
-
Even Function
A function for which f (- x) = f (x) for all x in the domain. This function is symmetric with respect to the y-axis.
-
Function
A rule which assigns to each element x in the domain a single element y in the range.
-
Horizontal Line Test
A graphical test to determine whether a function can be considered a one-to-one function. If no horizontal line drawn on the graph of the function passes through more than one point, then the function is a one-to-one function.
-
Intermediate Value Theorem
If f is a continuous function on a closed interval [a, b], then for every value r that lies between f (a) and f (b), there exists a constant c on (a, b) such that f (c) = r.
-
Interval Notation
A convenient way of representing sets of numbers on a number line bound by two endpoints. See closed interval and open interval.
-
Left-Hand Limit
This is the one-sided limit obtained by allowing the variable x to approach the constant c from "the left side" only, i.e. from values of x less than c.
-
Limit
This is the single value that a function f (x) approaches as the variable x approaches a constant c. Ordinarily, the term "limit" used by itself refers to a two-sided limit.
-
Linear Function
This is a polynomial function of the first degree. The variable x is only raised to the first power. The graph of this function is always a straight line. The function is of the form f (x) = ax + b where a and b are constants.
-
Odd Function
This is a function f for which f (- x) = - f (x) for all x in the domain. The graph of this function is symmetric with respect to the origin.
-
One-Sided Limit
This is the sort of limit that is obtained when the variable x is allowed to approach the constant c from only one side, i.e. from values greater than c or values less than c, but not both. One-sided limits can be either a left-hand limit or right-hand limit.
-
One-to-One Function
This is a type of function that assigns a different element in the range to each element in the domain so that no two domain elements map to the same range element. A graphical way to test for a one-to-one function is to perform the horizontal line test.
-
Open Interval
A set of numbers on the number line that is bounded by two endpoints and that does not include the endpoints. For example, the open interval (- 2, 2) contains all the numbers greater than -2 and less than 2, but does not include -2 and 2 themselves. An open endpoint is denoted by a parenthesis around the endpoint. Intervals may also be open at one endpoint and closed at the other.
-
Piecewise-Defined Function
A function that is defined differently for different intervals in its domain.
-
Polynomial Function
Any function of the form
f (x) = a0 + a1x + a2x2 + ....an-1xn-1 + anxn
where a0, a1, a2,...an are constants and n is a nonnegative integer. n denotes the "degree" of the polynomial. Examples of polynomial functions of varying degrees include constant functions, linear functions, and quadratic functions. -
Quadratic Function
A polynomial function of the second degree. The highest power that the variable x is raised to is the second power. These functions are of the form f (x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are constants.
-
Range
This is the set of all possible outputs for the function f.
-
Rational Function
This is a function of the form
r(x) = 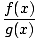
where f and g are both polynomial functions. -
Right-Hand Limit
This is the one-sided limit obtained by allowing the variable x to approach the constant c from "the right side" only, i.e. from values of x greater than c.
-
Squeeze Rule
A method for finding the limit of a function h(x): Suppose f (x)≤h(x)≤g(x) for all x in an open interval containing c (except possibly at c itself). If
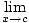 f (x) =
f (x) = 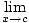 g(x) = L
g(x) = L
then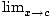 h(x) exists, and
h(x) exists, and
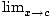 h(x) = L.
h(x) = L.
-
Two-sided Limit
A kind of limit in which x is allowed to approach c from values less than c and values greater than c with the exact same result. Thus, the two-sided limit exists only when both one-sided limits exist and are equal.
-
Vertical Line Test
A graphical test used to determine whether a rule is a function. If we cannot draw a vertical line through more than one point on a graph, then that graph represents a function.













