Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!

Annual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
You could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

SAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Properties of Polygons
One property of all convex polygons has to do with the number of
diagonals that it has:
Every convex polygon with n sides has n(n-3)/2 diagonals.
With this formula, if you are given either the number of diagonals or the number
of sides, you can figure out the unknown quantity. Diagonals become useful in
geometric proofs when you may need to draw in extra
lines or
segments, such as diagonals.
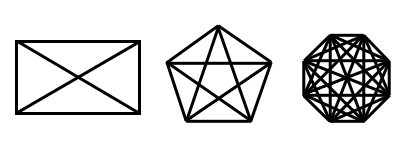
The interior angles of polygons follow certain patterns based on the number of sides, too. First of all, a polygon with n sides has n vertices, and therefore has n interior angles. The sum of these interior angles is equal to 180(n-2) degrees. Knowing this, given all the interior angle measures but one, you can always figure out the measure of the unknown angle.
An exterior angle on a polygon is formed by extending one of the sides of the polygon outside of the polygon, thus creating an angle supplementary to the interior angle at that vertex. Because of the congruence of vertical angles, it doesn't matter which side is extended; the exterior angle will be the same.
The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon (remember only convex polygons are being discussed here) is 360 degrees. This is a result of the interior angles summing to 180(n-2) degrees and each exterior angle being, by definition, supplementary to its interior angle. Take, for example, a triangle with three vertices of 50 degrees, 70 degrees, and 60 degrees. The interior angles sum to 180 degrees, which equals 180(3-2). Because the exterior angles are supplementary to the interior angles, they measure, 130, 110, and 120 degrees, respectively. Summed, the exterior angles equal 360 degreEs.
A special rule exists for regular polygons: because they are equiangular, the exterior angles are also congruent, so the measure of any given exterior angle is 360/n degrees. As a result, the interior angles of a regular polygon are all equal to 180 degrees minus the measure of the exterior angle(s).
Notice that the definition of an exterior angle of a polygon differs from that of an exterior angle in a plane. A polygon's exterior angle is not equal to 360 degrees minus the measure of the interior angle. A polygon's interior and exterior angles at a given vertex don't span the entire plane, they only span half the plane. That is why they are supplementary--because their measures sum to 180 degrees instead of 360.
Please wait while we process your payment





