Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



Create Account
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Log into your PLUS account
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Select Your Plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + tax
Annual
$29.99
/year + taxAnnual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + taxYou could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

Annual
$29.99
/year + taxSAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Annual
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
Annual
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Payment Information
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Thank You!
Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their membership. They will be prompted to log into an existing account or to create a new account. All members under 16 will be required to obtain a parent's consent sent via link in an email.Your Child’s Free Trial Starts Now!
Thank you for completing the sign-up process. Your child’s SparkNotes PLUS login credentials are [email] and the associated password. If you have any questions, please visit our help center.Your Free Trial Starts Now!
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment
Month
Day
Year
Please read our terms and privacy policy
Please wait while we process your payment

Overview of Post-Transcriptional RNA Splicing
Prokaryotic DNA transcription produces messenger RNA, which is necessary for transfer from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm where translation occurs. In contrast, eukaryotic DNA transcription takes place in a cell's nucleus and produces what is called a primary RNA transcript or pre-messenger RNA. Before eukaryotic products of transcription can be moved into the cytoplasm, they must undergo modifications that allow them to become mature messenger RNA. Splicing is the name given to the reaction that removes unnecessary segments of the primary RNA transcript, called introns. The removal of the introns produces mRNA (see the figure, below). Messenger RNA contains only exons, those portions of the primary RNA transcript that will be translated into a protein.
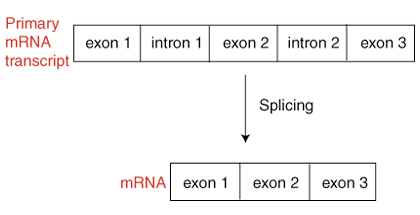
Unlike the sequence of an exon, intron sequences are unimportant. Only small portions of an intron sequence are preserved. These portions, located near the end of each intron, serve to identify a sequence as an intron, identifying the sequence for removal. There are intron identifying portions:
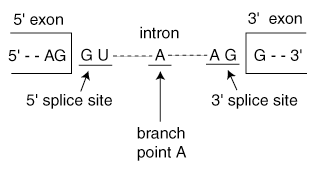
With the help of the spliceosome, a multi-component protein, the splicing reaction occurs in two steps. The spliceosome contains five small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPS, pronounced "snurps"). They are called U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6. Each snRNP contains protein components that are critical for the splicing reaction. U1 binds directly to the 5' splice site via complementary base pairing. U1 then recruits U2, which forms a complex with branch point A. U4 and U6 work in concert to form a "pre-splicing complex" and U5 helps to hold the exons in place between the first and second steps in the splicing reaction. Once the splicing reactions have occurred and the exons have been joined, the resulting mRNA is freed from the spliceosome machinery and the different snRNP components are recycled for further use.
In addition to the post-transcriptional modifications already discussed (5' cap, poly A tail addition, and splicing), a fourth type of modification can be made: RNA editing. RNA editing is a modification that changes the mRNA sequence and as a result alters the protein produced by that mRNA. Editing can occur in two ways. First, by changing one nucleotide to another, and second by inserting or deleting a nucleotide or nucleotides.
Please wait while we process your payment





