Compound Interest and the Natural Logarithm
One of the uses of e is in computing compound interest, using the equation
A = Pert, where:
P = the amount of money in the original account,
r = the yearly interest rate,
t = the number of years the money is in the account, and
A = the amount of money in the account after
t years.
Example 1: If $600 is put into an account which yields a yearly
compound interest rate of 8.6%, how much money is in the account at the end of 4
years?
A = Pert = 600e(0.086)(4) = 600e0.344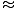 600(1.411) = $846.35
600(1.411) = $846.35
The account has $846.35 at the end of 4 years.
Example 2: If $1000 is put into an account for 6 years, it yields
$1822.12. What is the yearly compound interest rate of the account?
A = Pert
1822.12 = 1000er(6)
1.82212 = e6r
ln 1.82212 = ln e6r
0.6 = 6r
r = 0.1
The interest rate of the account is 10%.