-
Torsional Oscillator
The oscillation of any object suspended by a wire and rotating about the axis of the wire.
-
Pendulum
The classic pendulum consists of a particle suspended from a light cord. When the particle is pulled to one side and released, it swings back past the equilibrium point and oscillates between two maximum angular displacements.
-
Damping force
A force proportional to the velocity of the object that causes it to slow down.
-
Resonance
The phenomena in which a driving force causes a rapid increase in the amplitude of oscillation of a system.
-
Resonant Frequency
The frequency at which a driving force will produce resonance in a given oscillating system.
Terms
Formulae
| Equation for the torque felt in a torsional oscillator | τ = - κσ |
| Equation for angular displacement of a torsional oscillator | θ = θmcos(σt) |
| Equation for the period of a torsional oscillator | T = 2Π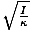 |
| Equation for the angular frequency of a torsional oscillator | σ = 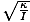 |
| Equation for the force felt by a pendulum | F = mg sinθ |
| Approximation of the force felt by a pendulum | F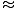 - ( - (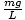 )x )x |
| Equation for the period of a pendulum | T = 2Π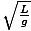 |
| Differential equation describing damped motion | kx + b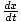 + m + m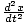 = 0 = 0 |
| Equation for the displacement of a damped system | x = xme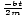 cos(σâ≤t) cos(σâ≤t) |
| Equation for the angular frequency of a damped system | σâ≤ = 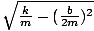 |













