The Law of Sines states that each side of a triangle is proportional to the
sine of the opposite angle. It looks like this:
The law of sines can be used when two angles and a side of a triangle are known.
Consider the following problem, in which we have two angles and the side
opposite one of them: A = 35o, B = 49o, and a = 7. The first part
we calculate is the third angle, C. C = 180o -35o -49o = 96o. Then, using the Law of Sines, b and c can be calculated.
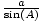 =
= 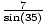 =
= 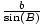 =
= 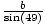 =
= 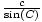 =
= 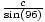 . b
. b 9.21,
and c
9.21,
and c 12.13.
12.13.
Now we'll consider two angles and the side included: A = 27o,
B = 105o, and c = 13. First we'll calculate the measure of the third angle,
C. C = 180o -27o -105o = 48o. Then using the Law of
Sines, a and b can be calculated, much like we did in the previous example.