Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



Create Account
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Log into your PLUS account
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Select Your Plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + tax
Annual
$29.99
/year + taxAnnual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + taxYou could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

Annual
$29.99
/year + taxSAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Annual
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
Annual
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Payment Information
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Thank You!
Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their membership. They will be prompted to log into an existing account or to create a new account. All members under 16 will be required to obtain a parent's consent sent via link in an email.Your Child’s Free Trial Starts Now!
Thank you for completing the sign-up process. Your child’s SparkNotes PLUS login credentials are [email] and the associated password. If you have any questions, please visit our help center.Your Free Trial Starts Now!
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment
Month
Day
Year
Please read our terms and privacy policy
Please wait while we process your payment

Colligative Properties
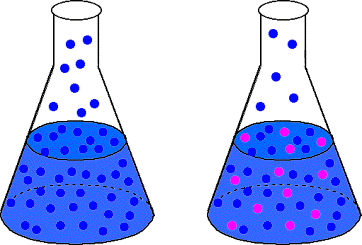
The French chemist Francois Raoult discovered the law that mathematically describes the vapor pressure lowering phenomenon. Raoult's law is given in :

Raoult's law states that the vapor pressure of a solution, P, equals the mole fraction of the solvent, csolvent, multiplied by the vapor pressure of the pure solvent, Po. While that "law" is approximately obeyed by most solutions, some show deviations from the expected behavior. Deviations from Raoult's law can either be positive or negative. A positive deviation means that there is a higher than expected vapor pressure above the solution. A negative deviation, conversely, means that we find a lower than expected vapor pressure for the solution. The reason for the deviation stems from a flaw in our consideration of the vapor pressure lowering event--we assumed that the solute did not interact with the solvent at all. That, of course, is not true most of the time. If the solute is strongly held by the solvent, then the solution will show a negative deviation from Raoult's law because the solvent will find it more difficult to escape from solution. If the solute and solvent are not as tightly bound to each other as they are to themselves, then the solution will show a positive deviation from Raoult's law because the solvent molecules will find it easier to escape from solution into the gas phase.
Solutions that obey Raoult's law are called ideal solutions because they behave exactly as we would predict. Solutions that show a deviation from Raoult's law are called non-ideal solutions because they deviate from the expected behavior. Very few solutions actually approach ideality, but Raoult's law for the ideal solution is a good enough approximation for the non- ideal solutions that we will continue to use Raoult's law. Raoult's law is the starting point for most of our discussions about the rest of the colligative properties, as we shall see in the following section.
One consequence of Raoult's law is that the boiling point of a solution made of a liquid solvent with a nonvolatile solute is greater than the boiling point of the pure solvent. The boiling point of a liquid or is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of that liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. For a solution, the vapor pressure of the solvent is lower at any given temperature. Therefore, a higher temperature is required to boil the solution than the pure solvent. is a phase diagram for both a pure solvent and a solution of that solvent and a nonvolatile solute that explains that point graphically.
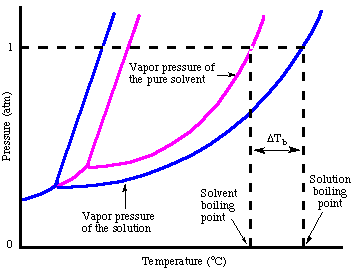
As you can see in the the vapor pressure of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent. Because both pure solvent and solution need to reach the same pressure to boil, the solution requires a higher temperature to boil. If we represent the difference in boiling point between the pure solvent and a solution as ΔTb, we can calculate that change in boiling point from the :
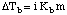
In the we use the units molality, m, for the concentration, m, because molality is temperature independent. The term Kb is a boiling point elevation constant that depends on the particular solvent being used. The term i in the above equation is called the van't Hoff factor and represents the number of dissociated moles of particles per mole of solute. The van't Hoff factor is 1 for all non-electrolyte solutes and equals the total number of ions released for electrolytes. Therefore, the value of i for Na2SO4 is 3 because that salt releases three moles of ions per mole of the salt.
Please wait while we process your payment





