Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



Create Account
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Log into your PLUS account
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Select Your Plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + tax
Annual
$29.99
/year + taxAnnual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + taxYou could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

Annual
$29.99
/year + taxSAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Annual
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
Annual
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Payment Information
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Thank You!
Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their membership. They will be prompted to log into an existing account or to create a new account. All members under 16 will be required to obtain a parent's consent sent via link in an email.Your Child’s Free Trial Starts Now!
Thank you for completing the sign-up process. Your child’s SparkNotes PLUS login credentials are [email] and the associated password. If you have any questions, please visit our help center.Your Free Trial Starts Now!
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment
Month
Day
Year
Please read our terms and privacy policy
Please wait while we process your payment

Problems
Problem :
What is profitability? Describe it in your own words. How is it calculated?
Profitability is the measure of the net energy gain from eating a food source. Energy is expended in handling the foot item, and energy is gained by eating the food item. Handling time may waste valuable time searching for and consuming other items. Profitability is calculated as E/h, the energy gained by eating the item divided by the time handling the item.
Problem :
You are standing in front of a McDenny's and it is dinner time. You consider ordering chicken nuggets, but you are very hungry and not quite sure they will satisfy you. There is a supermarket not too far away, it would probably take you 30 minutes to go to the supermarket and buy a steak. And while the steak has 500 calories, it also takes 20 minutes to cook. The line at McDenny's is not too long, and it will only take you about 7 minutes to get your food, but chicken nuggets only contain 220 calories. Should you stay and order the nuggets or go to the supermarket and get a steak?
The profitability, E/h of chicken nuggets is 220/7= 31.4. E/T for the steak is 500/(20+30)= 10. You should eat the nuggets; you know you want to.
Problem :
You are walking in the woods, and are very hungry. Berries are very plentiful where you are, but the do not contain as many calories as apples, which are not quite as easy to find. As you are walking along, you come across an apple tree. Should you spend your time eating the apple, or spend your time eating berries, which you would be able to eat continuously?
You should eat the apple. You should always eat the more profitable food source if you find it. The contingency theory assumes you have the less profitable food item in front of you and are deciding whether to eat it or search for better food items. If you have found the more profitable food item, it always pays to eat it.
Problem :
Describe in your own words why an animal should leave a food patch when the rate of consumption lowers beyond a certain point.
As an animal consumes the food in a given patch, the food in that patch becomes scarcer, and so the rate of consumption decreases, even though the total consumption is still increasing. After the optimal time to stay at any one patch, it would be more profitable to search for a fresh patch where the rate of consumption would be much higher.
Problem :
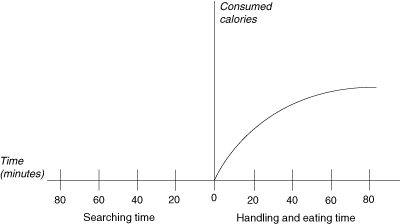
The above graph shows you the rate of calorie consumption as a function of time spent at one food source. Food is running out, and you know there is another, completely fresh source about 70 minutes away. What is the total time you should spend at the source you are currently at before leaving for a new source?
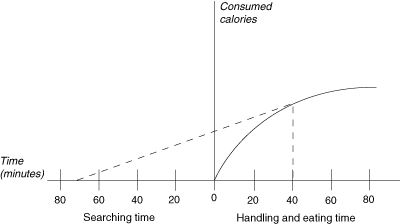
We know the search time until we find the next source is 70 minutes. We draw a line from 70 minutes that is tangent to the curve, and we find that it touches the curve at a handling time of 40 minutes. This means that after we have been at our current food source for 40 minutes, we should leave for the new source.
Please wait while we process your payment





