Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!

Annual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
You could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

SAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Eukaryotic Organelles: The Cell Nucleus, Mitochondria, and Peroxisomes
The endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, is a very important cellular structure because of its function in protein synthesis and lipid synthesis. For example, the ER is the site of production of all transmembrane proteins. Since nearly all proteins that are secreted from a cell pass through it, the ER is also important in cellular trafficking. In addition to these major roles, the ER plays a role in a number of other biological processes. There are two different types of ER: smooth ER and rough ER (RER).
The rough ER has its name because it is coated with ribosomes, the structures most directly responsible for carrying out protein synthesis. Smooth ER lacks these ribosomes and is more abundant in cells that are specific for lipid synthesis and metabolism.

In addtion to protein and lipid synthesis, the ER also conducts post-synthesis modifications. One such modification involves the addition of carbohydrate chains to the proteins, though the function of this addition is unknown. Another major modification is called protein folding, whose name is rather self- explanatory. Another role of the ER is to capture calcium for the cell from the cytosol. Finally, the ER can secrete proteins into the cell that are usually destined for the golgi apparatus.
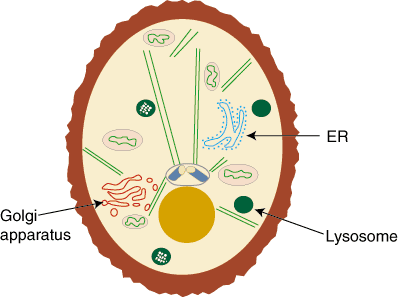
The golgi apparatus is usually located near the cell nucleus. It is composed of a series of layers called golgi stacks. Proteins from the ER always enter and exit the golgi apparatus from the same location. The cis face of the golgi is where proteins enter. A protein will make its way through the golgi stacks to the other end called the trans face where it is secreted to other parts of the cell.
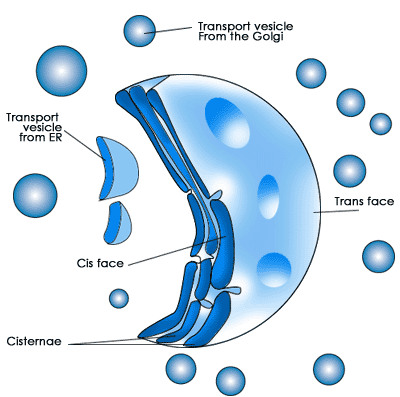
In the golgi apparatus, more carbohydrate chains are added to the protein while other chains are removed. The golgi stacks also sort proteins for secretion. After sorting, the membrane of the golgi buds off, forming secretory vesicles that transport proteins to their specific destination in the cell. A protein's destination is often signaled with a specific amino acid sequence at its end. A protein secretion most often travels back to the ER, to the plasma membrane where it can become a transmembrane protein, or to the next structure we will discuss, the lysosomes.
Lysosomes are sites of molecular degradation found in all eukaryotic cells. They are small, single-membrane packages of acidic enzymes that digest molecules and are found throughout eukaryotic cells. As such, Lysosomes are a sort of cellular "garbage can," getting rid of cellular debris. Proteins that are not correctly folded or have significant mutations can be secreted to the lysosomes and be degraded instead of taking up space in the cell. Detritus proteins and other molecules can find their way to the lysosome in a variey of ways.
Please wait while we process your payment





