Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!

Annual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
You could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

SAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Prokaryotic DNA Transcription Elongation and Termination
The elongation phase of transcription refers to the process through which nucleotides are added to the growing RNA chain. As the RNA polymerase moves down the DNA template strand, the open complex bubble moves also. The bubble is of a fixed number of nucleotides, meaning that at the leading end of the bubble the DNA helix is being unwound, while at its trailing end the single strands are being rejoined. Whereas separation of the DNA helix is permanent in replication, it is only temporary in transcription. depicts the beginning steps in transcription up to elongation and the relative positions of the bubble and the polymerase holoenzyme.
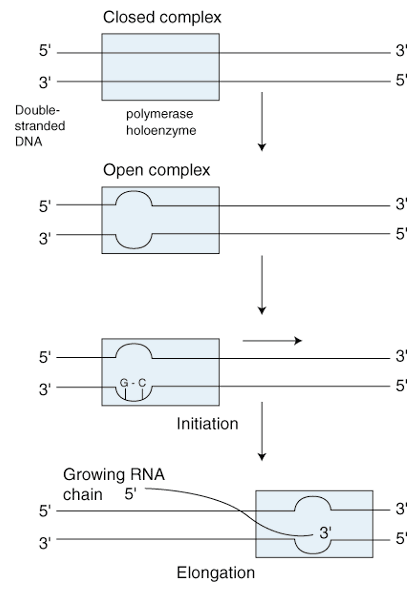
As the figure shows, within the open complex bubble the DNA and RNA form a hybrid or joint complex. The exact length of this region is unknown, but it is thought to be between 3 and 12 base pairs long and is found at the growing 3' end of the RNA. The figure also illustrates how the 5' tail end of the RNA chain is separate from, as opposed to base paired to, the DNA template strand. This is another difference between DNA replication and DNA transcription; in replication, the newly synthesized DNA strand remains bound in a helix to the strand with which it has base paired. After the initial stretch of approximately 8 base pairs has been synthesized, the sigma unit, which is responsible for recognition and binding to the promoter region, is released. The core enzyme is left to polymerize the growing RNA chain alone. This leads to the continuous extrusion of the 5' end of the RNA from the enzyme complex. At normal room temperature, the rate of transcription in prokaryotes is 40 nucleotides per second.
RNA synthesis will continue along the DNA template strand until the polymerase encounters a signal that tells it to stop, or terminate, transcription. In prokaryotes, this signal can take two forms, rho-independent and rho-dependent.
The rho-independent terminator is the more simple of the two systems and as a result is also called simple termination. The rho-independent signal is found on the DNA template strand and consists of a region that contains a section that is then repeated a few base pairs away in the inverted sequence.
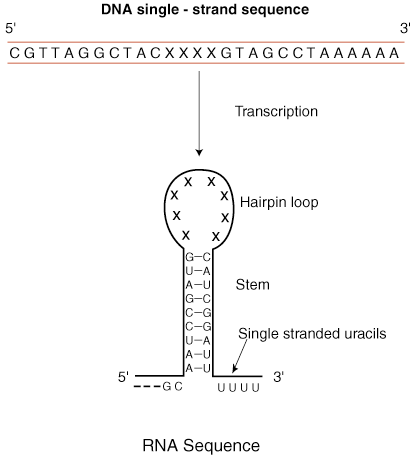
As is shown in the figure, the patch is followed by a short string of adenines. When this stretch is transcribed into an RNA sequence, the RNA can fold back and base pair with itself forming a hairpin loop.
As you can see, the string of adenines in the DNA sequence are transcribed into uracils in the RNA sequence. Because the uracil bases will only pair weakly with the adenines, the RNA chain can easily be released from the DNA template, terminating transcription.
Please wait while we process your payment





