Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment
Get instant, ad-free access to our grade-boosting study tools with a 7-day free trial!
Learn more



Create Account
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Log into your PLUS account
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Select Your Plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + tax
Annual
$29.99
/year + taxAnnual
2-49 accounts
$22.49/year + tax
50-99 accounts
$20.99/year + tax
Select Quantity
Price per seat
$29.99 $--.--
Subtotal
$-.--
Want 100 or more? Request a customized plan
Monthly
$5.99
/month + taxYou could save over 50%
by choosing an Annual Plan!

Annual
$29.99
/year + taxSAVE OVER 50%
compared to the monthly price!
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Annual
$22.49/month + tax
Save 25%
on 2-49 accounts
Annual
$20.99/month + tax
Save 30%
on 50-99 accounts
| Focused-studying | ||
| PLUS Study Tools | ||
| AP® Test Prep PLUS | ||
| My PLUS Activity | ||
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Testimonials from SparkNotes Customers
No Fear provides access to Shakespeare for students who normally couldn’t (or wouldn’t) read his plays. It’s also a very useful tool when trying to explain Shakespeare’s wordplay!
Erika M.
I tutor high school students in a variety of subjects. Having access to the literature translations helps me to stay informed about the various assignments. Your summaries and translations are invaluable.
Kathy B.
Teaching Shakespeare to today's generation can be challenging. No Fear helps a ton with understanding the crux of the text.
Kay H.
Create Account
Select Plan
Payment Info
Start 7-Day Free Trial!
Payment Information
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial.
If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
You will only be charged after the completion of the 7-day free trial. If you cancel your account before the free trial is over, you will not be charged.
Order Summary
Annual
7-day Free Trial
SparkNotes PLUS
$29.99 / year
Annual
Quantity
51
PLUS Group Discount
$29.99 $29.99 / seat
Tax
$0.00
SPARK25
-$1.25
25% Off
Total billed on Nov 7, 2024 after 7-day free trail
$29.99
Total billed
$0.00
Due Today
$0.00
Promo code
This is not a valid promo code
Card Details
By placing your order you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
By saving your payment information you allow SparkNotes to charge you for future payments in accordance with their terms.
Powered by stripe
Legal
Google pay.......



Thank You!
Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their membership. They will be prompted to log into an existing account or to create a new account. All members under 16 will be required to obtain a parent's consent sent via link in an email.Your Child’s Free Trial Starts Now!
Thank you for completing the sign-up process. Your child’s SparkNotes PLUS login credentials are [email] and the associated password. If you have any questions, please visit our help center.Your Free Trial Starts Now!
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Sorry, you must enter a valid email address
By entering an email, you agree to our privacy policy.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment
Month
Day
Year
Please read our terms and privacy policy
Please wait while we process your payment

Ionic Bonding
When a highly electronegative atom and an electropositive one are bonded together, an electron is transferred from the electropositive atom to the electronegative atom to form a cation and an anion, respectively. The cation, being a positively charged ion, is attracted to the negatively charged anion as described by Coulomb's law:
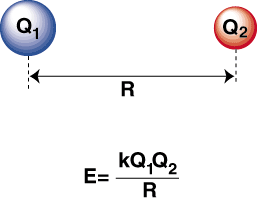
A negative energy means there is an attractive interaction between the particles in the . If the charges on the two ions are opposite in sign, they will attract each other. Conversely, if two charges are similar, they repel each other. Using this knowledge we can construct a graph of energy versus distance for two oppositely charges ions. At large distances, there is a negligible energy of attraction between the two ions, but as they are brought closer together, they are attracted to one another. Coulomb's law may seem to predict that the ions should be as close as possible to achieve a minimal energy state. However, the shows that the ions are actually repelled at small distances. To explain this observation, remember that the ions' nuclei are both positively charged. When the nuclei approach each other, they repel strongly--accounting for the steep rise in potential as the ions get closer than the bond length.
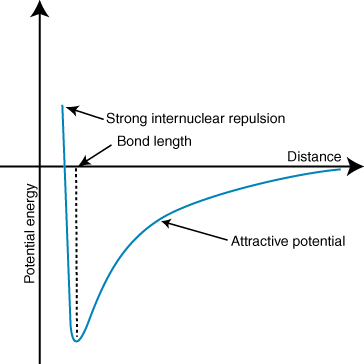
The depth (y-axis) of the minimum in the potential energy curve above represents the bond strength, and the distance (x-axis) at the energy minimum is the bond length. Using Coulomb's law and the bond length, one can actually predict with some accuracy the strength of an ionic bond. Performing a series of these calculations you find that ionic compounds formed by ions with larger charges create stronger bonds and that ionic compounds with shorter bond lengths form stronger bonds.
Ionic compounds do not usually exist as isolated molecules, such as LiCl, but as a part of a crystal lattice--a three dimensional regular array of cations and anions. Ionic compounds form lattices due to the contributing coulombic attractions of having each cation surrounded by several anions and each anion surrounded by several anions. An example of a crystal lattice is shown in :
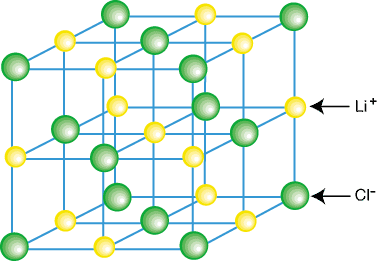
As you can see in the above figure, each lithium ion is surrounded by six chlorine atoms and vice versa. By virtue of the arrangement of the ions in the lattice, the lattice is lower in energy than it would be if the ions were separated into isolated LiCl molecules.
Please wait while we process your payment





