Problem :
A wire of length 10 cm carries a current of 5 esu/s parallel to a magnetic field of 10 gauss. What is the magnitude of the force on the wire?
Since the moving charges (in the wire) are moving parallel to the magnetic field, no net force acts on the wire.
Problem :
A wire of length 10 cm carries a current of 3×104 esu/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 10 gauss. What is the magnitude of the force on the wire?
Now the charges are moving perpendicular to the magnetic field, and the force on
the wire is given by our equation F = 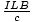 =
= 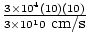 = 1×10-4 dynes. This small value shows
how small the effect of magnetic fields are in practical situations, and why the
relation between magnetic fields and current went undetected for such a long
time.
= 1×10-4 dynes. This small value shows
how small the effect of magnetic fields are in practical situations, and why the
relation between magnetic fields and current went undetected for such a long
time.
Problem :
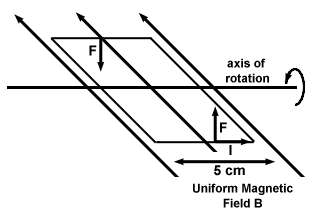
A wire in the shape of a square with sides 5 cm carries a current of 1 amp, or
3×109 esu/sec in a plane parallel to a magnetic field of 100 gauss, as
shown below. What is the net force on the wire? What is the net torque?
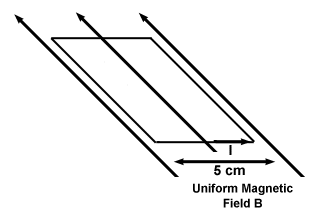
To find the force on the wire we must look at each part of the wire
individually. There are four sections: each side of the square. The current in
two sections moves parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field, and thus
experience no force. The other two sections have a current perpendicular to the
magnetic field, and each segment experiences a force of
F = 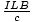 =
= 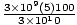 = 50 dynes. However,
because the current flows in opposite directions, the forces are in opposite
directions and there is no net force on the wire.
= 50 dynes. However,
because the current flows in opposite directions, the forces are in opposite
directions and there is no net force on the wire.
What about torque, though? If we designate an axis of rotation through the
wire, as shown below, both forces act to rotate the wire in the same direction.
Problem :
In CGS units, F = 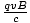 . What does this equation convert to in SI units?
. What does this equation convert to in SI units?
Clearly the same physical quantities of q, v, and B must be involved, but the factor of 1/c might be changed. Consider a particle of 1 coulumb (3×109 esu) traveling at a speed of 1 m/s (100cm/s) in a uniform field of 1 Tesla (10000 gauss). Using the formula we know (CGS units), the force in this situation is:
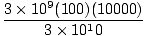 = 105 dynes
= 105 dynes
| F = qvB |


 payment page
payment page



