-
Diffraction
Due to interference effects between waves, wavefronts appear to bend around obstacles and spread out after passing through narrow apertures. In fact, any deviation of light from propagation in a straight line is termed diffraction. In general, it occurs wherever light waves encounter some opaque obstacle. The energy density re-distribution caused by the interference effects caused by the obstacle are called a diffraction pattern.
-
Interference
When two or more light waves occupy the same position in space their amplitudes add according to the principle of superposition. Because the irradiance of light varies according to the square of the amplitude, it is possible for the irradiance resulting from the overlap of two waves to differ from the sum of the component irradiances. When this occurs, the effect is called interference, and the resulting energy distribution is an interference pattern.
-
Polarization
The polarization of light refers to the plane in which the electric field of a light ray oscillates. Light in which the electric field vector oscillates in any one fixed plane is said to be plane polarized or linearly polarized. In natural light, as well as light from most incandescent sources the direction of the electric field direction changes rapidly in time, as a result of the superposition of many waves linearly polarized in different planes--such light is said to be randomly polarized.
-
Irradiance
(deonoted I) Commonly known as intensity, the irradiance of light corresponds to the average energy per unit area per unit time, or the power per unit area imparted by a light ray. In a straighforward sense, it is the 'amount' of light or the brightness. It is equal to the time average of the Poynting vector:
I = < S > = 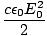 = ε0c < E2 > =
= ε0c < E2 > = 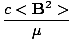
-
Coherent
Sources which produce light rays which have a constant phase difference (that may or may not be zero) are said to be coherent. The notion of a perfectly monochromatic source (one that produces a single frequency only) is an unattainable idealization, and any real light wave will contain a (perhaps very small) band of frequencies. The amount of time over which such a band of frequencies can be usefully approximated by a sinusoidal wave is called the coherence time. The distance light travels during this time, behaving in a predictable and sinusoidal way is called the coherence length of the source. The narrower the band of frequencies emitted, the longer the coherence length.
-
Fringes
Interference and diffraction effects usually produce a series of alternately bright and dark regions. These regions are not sharply defined as the irradiance varies constantly with position. These regions of maximum and minimum irradiance are called bright and dark fringes respectively.
-
Plane polarized
When the electric field vector of a light oscillates in a single, fixed plane, constant in time, it is said to be plane polarized or linearly polarized.
-
Plane of vibration
The plane containing the electric field vector and the vector k defining the direction of propagation. For a linearly polarized light wave, the plane remains fixed.
-
Circularly polarized
This arises when the phase difference between the two component waves differ by a factor of ε = - Π/2±2mΠ for right-circularly polarized light, and ε = Π/2±2mΠ for left-circularly polarized light, and the amplitudes of the electric fields of the two waves are equal. In this case the electric field vector rotates around a the axis defined by the direction of propagation (clockwise for right-polarized and counterclockwise for left) at a constant angular frequency.
-
Transmission axis
The transmission axis of a polarizer is the axis such that light with its electric field oriented parallel to this axis will be transmitted. If the light is not already linearly polarized parallel to the transmission axis, only that component of the light parallel to the axis will pass through the polarizer unhindered.
-
Polarizer
Any substance or device which transmits light preferentially according to its polarization. In other words, a substance whose input is natural light and output is polarized light. Polarizers can be linear, circular or partial depending on the type and extent of polarization they produce.
-
Analyzer
Any polarizer used as a tool to determine the polarization of light. For example, if one polarizer is placed behind another in order to determine the transmission axis of the first polarizer, the second polarizer is called an analyzer.
-
Dichroic
Many polarizers are dichroic: they absorb light selectively depending on polarization. Such dichroism must be the result of an inherent anisotropy in the structure of the material. There are a variety of crystals and minerals that are dichroic.
-
Birefringence
Refers to substances that have different optical properties along different axes through the substance. The structure of a crystal may allow electrons or atoms to vibrate much more easily in one direction than in another, causing the speed of light to be different, depending the direction in which a substance is traversed by a light ray. This causes the refractive index of the material to be different along different axes. This must arise as a result of an anisotropy in the material.
-
Brewster's angle
(also called the polarization angle) Referring to polarization by reflection, the angle tanθp = nt/ni for which an incident ray with its electric field oscillating in the incident plane exhibits no reflected ray. This causes randomly polarized light incident at this angle to become completely polarized in the direction perpendicular to the incident plane upon reflection.













