-
Chemical Potential
The Chemical Potential is defined such that:
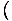
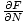
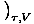 .
.
-
Enthalpy
The Enthalpy, H, is defined as H = U = pv and its identity is dH = τ dσ + V dp + μ dN.
-
Extensive
An extensive variable of a system doubles upon duplication of the system. Important extensive variables are the volume V, the entropy σ, the number N and the energy U. Compare to intensive variables.
-
Gibbs Free Energy
The Gibbs Free Energy, G, is defined as G = U - τσ + pV and its identity is dG = - σ dτ + V dp + μ dN.
-
Helmholtz Free Energy
The Helmholtz Free Energy, F, is defined as F = U - τσ and its identity is dF = - σ dτ - p dV + μ dN.
-
Intensive
An intensive variable of a system remains constant upon duplication of the system. Important intensive variables are the temperature τ, the chemical potential μ, and the pressure p. Compare to extensive variables.
-
Legendre Transform
The Legendre Transform is a mathematical tool that we employ to change variables in expression of then energy, such as defining F = U - τσ in order to change variables from σ to τ in the energy.
-
Maxwell Relations
The Maxwell Relations give relationships between the partial derivative of one variable with respect to a variable in a different pairing and the corresponding cross partial derivative of the other variable in the second pairing with respect to the other variable in the first.
-
Pressure
The pressure is defined such that: p = -
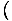
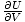
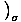 , and is one of the important intensive variables in thermodynamics.
, and is one of the important intensive variables in thermodynamics.
-
Thermodynamic Identity
The Thermodynamic Identity relates the energy U to the 6 variables we have discussed:
dU = τ dσ - p dV + μ dN













