Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews July 19, 2025 July 12, 2025
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Problems 3
Problem : Draw a monocot and a dicot stem, being sure to emphasize the differences in the arrangement of vascular tissue.
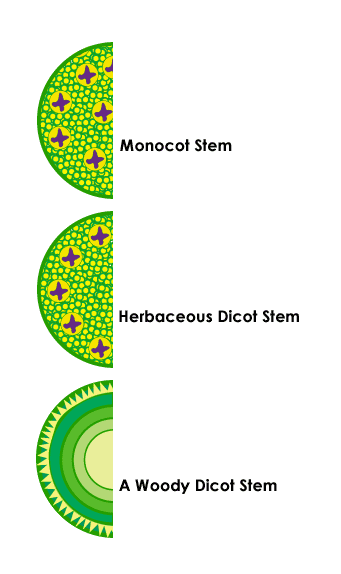
Problem : How does the vascular system in monocots expand when the plant grows?
As a monocot grows in size, discrete new vascular bundles are produced that are scattered throughout the new tissue.Problem : How does the vascular system in dicots expand when the plant grows?
As a dicot grows, existing vascular bundles grow larger. The vascular cambium in between the xylem and phloem produces new xylem and phloem cells, pushing the old cells outward and expanding the size of the bundle.Problem : What are herbaceous dicots? Woody dicots?
Herbaceous dicots (mostly annuals) have soft, non-woody stems. Woody dicots (mostly perennials, including most trees) have woody stems.Problem : Describe the features of a woody dicot's vascular system.
In mature woody dicots, the vascular bundles (composed of xylem, phloem, and vascular cambium) join together to form continuous rings around the interior of the stem. Woody dicots also develop a lateral system of nutrient transport in which vessels called rays extend horizontally from the phloem to the pith, carrying nutrients to the pith for storage or to the phloem for dispersal.Please wait while we process your payment

