-
Bimolecular
Involving two molecules. In this SparkNote, the term bimolecular is used to refer to SN2 and E2 reactions. The rate-limiting transition states of both reactions involve two molecules.
-
Carbocation
A carbon that carries a positive charge. Carbocations are highly unstable and are prone to rearrangement. SN1 and E1 reactions proceed through a common carbocation intermediate.
-
E1
A reaction where a β-hydrogen is Eliminated to form a double bond. E1 reactions go through a carbocation intermediate. Somewhat similar to the E2 reaction.
-
SN1
A reaction in which a Nucleophile Substitutes for a leaving group. SN1. It goes through a carbocation intermediate.
-
Secondary
A secondary carbon has bonds to two other carbons.
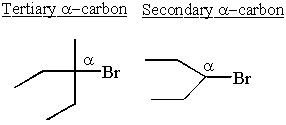
-
Tertiary
A tertiary carbon has bonds to three other carbons.
-
Unimolecular
Involving one molecule. This term is used synonymously with the E1 and SN1 reactions in this SparkNote. The rate-limiting transition states of both mechanisms involve one molecule.


 payment page
payment page



