Please wait while we process your payment
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
If you don't see it, please check your spam folder. Sometimes it can end up there.
Please wait while we process your payment

By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Don’t have an account? Subscribe now
Create Your Account
Sign up for your FREE 7-day trial
By signing up you agree to our terms and privacy policy.
Already have an account? Log in
Your Email
Choose Your Plan
Individual
Group Discount
Save over 50% with a SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan!
 payment page
payment page
Purchasing SparkNotes PLUS for a group?
Get Annual Plans at a discount when you buy 2 or more!
Price
$24.99 $18.74 /subscription + tax
Subtotal $37.48 + tax
Save 25% on 2-49 accounts
Save 30% on 50-99 accounts
Want 100 or more? Contact us for a customized plan.
 payment page
payment page
Your Plan
Payment Details
Payment Summary
SparkNotes Plus
You'll be billed after your free trial ends.
7-Day Free Trial
Not Applicable
Renews July 25, 2025 July 18, 2025
Discounts (applied to next billing)
DUE NOW
US $0.00
SNPLUSROCKS20 | 20% Discount
This is not a valid promo code.
Discount Code (one code per order)
SparkNotes PLUS Annual Plan - Group Discount
Qty: 00
SparkNotes Plus subscription is $4.99/month or $24.99/year as selected above. The free trial period is the first 7 days of your subscription. TO CANCEL YOUR SUBSCRIPTION AND AVOID BEING CHARGED, YOU MUST CANCEL BEFORE THE END OF THE FREE TRIAL PERIOD. You may cancel your subscription on your Subscription and Billing page or contact Customer Support at custserv@bn.com. Your subscription will continue automatically once the free trial period is over. Free trial is available to new customers only.
Choose Your Plan
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
For the next 7 days, you'll have access to awesome PLUS stuff like AP English test prep, No Fear Shakespeare translations and audio, a note-taking tool, personalized dashboard, & much more!
You’ve successfully purchased a group discount. Your group members can use the joining link below to redeem their group membership. You'll also receive an email with the link.
Members will be prompted to log in or create an account to redeem their group membership.
Thanks for creating a SparkNotes account! Continue to start your free trial.
We're sorry, we could not create your account. SparkNotes PLUS is not available in your country. See what countries we’re in.
There was an error creating your account. Please check your payment details and try again.
Please wait while we process your payment

Your PLUS subscription has expired
Please wait while we process your payment
Please wait while we process your payment

Quantity theory of money
What gives money value? We know that intrinsically, a dollar bill is just worthless paper and ink. However, the purchasing power of a dollar bill is much greater than that of another piece of paper of similar size. From where does this power originate?
Like most things in economics, there is a market for money. The supply of money in the money market comes from the Fed. The Fed has the power to adjust the money supply by increasing or decreasing the number of bills in circulation. Nobody else can make this policy decision. The demand for money in the money market comes from consumers.
The determinants of money demand are infinite. In general, consumers need money to purchase goods and services. If there is an ATM nearby or if credit cards are plentiful, consumers may demand less money at a given time than they would if cash were difficult to obtain. The most important variable in determining money demand is the average price level within the economy. If the average price level is high and goods and services tend to cost a significant amount of money, consumers will demand more money. If, on the other hand, the average price level is low and goods and services tend to cost little money, consumers will demand less money.
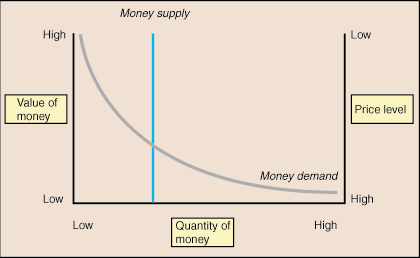
The value of money is ultimately determined by the intersection of the money supply, as controlled by the Fed, and money demand, as created by consumers. Figure 1 depicts the money market in a sample economy. The money supply curve is vertical because the Fed sets the amount of money available without consideration for the value of money. The money demand curve slopes downward because as the value of money decreases, consumers are forced to carry more money to make purchases because goods and services cost more money. Similarly, when the value of money is high, consumers demand little money because goods and services can be purchased for low prices. The intersection of the money supply curve and the money demand curve shows both the equilibrium value of money as well as the equilibrium price level.
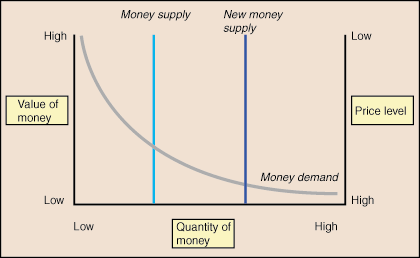
The value of money, as revealed by the money market, is variable. A change in money demand or a change in the money supply will yield a change in the value of money and in the price level. Notice that the change in the value of money and the change in the price level are of the same magnitude but in opposite directions. An increase in the money supply is depicted in Figure 2. Notice that the new intersection of the money supply curve and the money demand curve is at a lower value of money but a higher price level. This happens because more money is in circulation, so each bill becomes worth less. It takes more bills to purchase goods and services, and thus the price level increases accordingly.
The quantity theory of money is based directly on the changes brought about by an increase in the money supply. The quantity theory of money states that the value of money is based on the amount of money in the economy. Thus, according to the quantity theory of money, when the Fed increases the money supply, the value of money falls and the price level increases. In the SparkNote on inflation we learned that inflation is defined as an increase in the price level. Based on this definition, the quantity theory of money also states that growth in the money supply is the primary cause of inflation.
Please wait while we process your payment

