-
Absolute minimum
The least single value that a function attains on a given interval. A function f has an absolute minimum at x = b if f (b)≤f (x) for all x in the domain of f.
-
Absolute maximum
The greatest single value that a function attains on a given interval. A function f has an absolute maximum at x = b if f (b)≥f (x) for all x in the domain of f.
-
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity.
-
Average Rate of Change
For a function f (x), this represents the total change in f over a given interval divided by the total change in x.
-
Concave Down
A term applied to a section of the graph where the derivative is decreasing throughout.
-
Concave up
A term applied to a section of the graph where the derivative is increasing throughout.
-
Critical points
These are points in the domain of f where f'(x) = 0 or f'(x) is undefined.
-
Critical Point Theorem
If f has a local extremum at x = b, then (b, f (b)) is a critical point.
-
Distance
This is the scalar analog of the vector quantity position. The distance from a certain point is the absolute value of the position relative to that point. Thus, distances are always positive.
-
Horizontal asymptote
A horizontal line that the graph of f (x) approaches but never touches as x approaches positive or negative infinity.
-
Instantaneous rate of change
This is the rate of change of a function at a single point on its graph. The instantaneous rate of change of f at x = a is given by the derivative, f'(a).
-
Local extrema
The collective term for local maxima and local minima.
-
Local maximum
A function f has a local maximum at x = b if f (b) is the largest value that f attains "near b." More formally, a function f (x) has a local maximum at x = b if there is an open interval I in which f (b)≥f (x) for all x in I.
-
Local minimum
A function f has a local minimum at x = b if f (b) is the smallest value that f attains "near b." More formally, a function f (x) has a local minimum at x = b if there is an open interval I in which f (b)≤f (x) for all x in I.
-
Mean value theorem
If f is continuous on [a, b] and differentiable on (a, b), then there exists a point c on [a, b] for which
f'(c) = 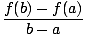
-
Position
This refers to the relative placement of an object with respect to another object, which is generally placed at the origin. This is a vector quantity, so it has both a magnitude and a direction.
-
Rectilinear motion
A type of motion along a straight line, normally depicted by a number line.
-
Relative extrema
Same as local extrema.
-
Relative maximum
Same as local maximum.
-
Relative minimum
Same as local minimum.
-
Rolle's theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b), and f (a) = f (b), then there is a c on (a, b) where f'(c) = 0. This is a special case of the mean value theorem.
-
Scalar quantities
These are quantities that only express a magnitude. They are often compared against vector quantities, which have a magnitude and a direction.
-
Speed
Speed is the scalar analog of velocity.
-
Vector quantities
These are quantities that have both a magnitude (indicated by the number) and a direction (indicated by the presence or absence of a negative sign). They are often compared against scalar quantities, which only have a magnitude. For example, velocity is the vector analog of speed, because while speed depends only on the magnitude of the motion, velocity also depends on the direction. So, whether one is traveling with a velocity of 3 miles per hour in the positive direction or in the negative direction, one still has a speed of 3 miles per hour.
-
Velocity
This is the rate of change of position.
-
Vertical asymptote
This is a vertical line that the graph approaches, but never touches. Near a vertical asymptote, a function approaches positive or negative infinity. A vertical asymptote occurs at x = c when the following are all true
1) f (c) is undefined
2)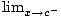 f (x) = ∞ or - ∞
f (x) = ∞ or - ∞
3)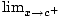 f (x) = ∞ or - ∞
f (x) = ∞ or - ∞


 payment page
payment page



