Terms
-
Rotational motion
The motion of any object in which every part of the object rotates about a
common axis in a circular path.
-
Angular displacement
The angle swept out by the circular motion of a particle. See definition of
angular displacement
-
Radians
A unit of measuring an angle. The relation between radians and degrees is as
follows:
| 1 revolution = 2Π radians = 360o |
|
-
Average angular velocity
The average rate at which an object rotates in a circular path. See
formula.
-
Instantaneous angular velocity
The instantaneous rate at which an object rotates in a circular path. See
formula.
-
Angular acceleration
The rate of change of angular velocity. See formula.
-
Right hand rule
The rule by which the direction of a rotational vector can be found: take your
right hand, curl your fingers and stick your thumb straight up. If you let the
curl of your fingers follow the path of the rotating particle or body, your
thumb will point in the direction of the angular velocity of the body.
Formulae
|
Definition of angular displacement
| μ = s/r |
|
Conversion between radians and degrees
| 2Π rad = 1 revolution = 360o |
|
Formula for average angular velocity
| 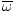 = = 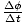 |
|
Formula for instantaneous angular velocity
| σ = 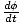 |
|
Formula for angular acceleration
| α = 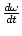 |
|
Kinematic equations for rotational motion
|
-
σf = σo + αt
-
μf = μo + σot +
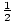 αt2 αt2
-
σf2 = σo2 +2αμ
-
μ =
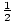 (σo + σf)t (σo + σf)t
|
|
Relation of linear and angular displacement
| s = μr |
|
Relation of linear and angular velocity
| v = σr |
|
Relation of tangential and angular acceleration
| aT = αr |
|
Relation of radial acceleration and angular velocity
| aR = σ2r |
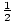 αt2
αt2
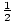 (σo + σf)t
(σo + σf)t
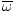 =
= 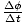
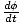


 payment page
payment page



