Based on the coefficients in a given a balanced equation, a certain ratio must exist between reactants in order to obtain a certain amount of product. This ratio is the mole ratio we discussed previously
However, now suppose that you simply want to make as much product as possible given the amounts of reactant you currently have. Suppose also that the amount of each reactant you have is not in the correct ratio. You find that you have an almost endless supply of the first of your two reactants, but very little of the second. What happens? Well, obviously, you are not going to be able to use all of the first reactant. It will only combine in ratio with the second; the excess will have nothing to react with. The amount of product you obtain will therefore be in ratio with the second reactant. Confused? An example is long overdue.
Problem: You have 10 g of solid carbon, but only 10 mL of pure oxygen
gas. Not all of the carbon will be used in the reaction. Given that the
reactants react according the following balanced equation, how many molecules of
CO2(g) can be produced? How many grams of C(s) will react?
How much C(s) is left over after all the oxygen is gone?
| C(s) + O2(g)→CO2(g) |
Solution: Let's answer the first question first. Start by converting to moles O2(g) [Note that oxygen is diatomic, so 10 mL of oxygen gas means 10 mL of O2(g)].
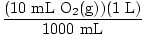 × ×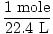 = 4.46×10-4 moles O2(g) = 4.46×10-4 moles O2(g) |
Did you remember to convert milliliters to liters? If so, remember to carry your units. Now, since our mole ratio between O2(g) and CO2(g) is 1:1, we can move to the last step.
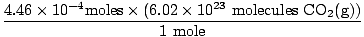 = 2.68×1020 molecules CO2(g) = 2.68×1020 molecules CO2(g) |
Now let's figure out how many grams of C(s) react. How do we figure this out? Well, how many moles of C(s) will react with 4.46×10-4 moles of O2(g)? Mole ratio tells us that an equal number of moles will react. Therefore,
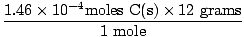 = 5.352×10-3 grams C(s) = 5.352×10-3 grams C(s) |
It is a simple matter of subtraction to figure out how much C(s) is left over.
| 10 grams C(s) -5.352×10-3 grams C(s) = 9.995 grams C(s) |
There was not enough oxygen to react with all the carbon. For this reason, we would call oxygen the limiting reagent of the reaction. As the name implies, the limiting reagent limits or determines the amount of product that can be formed. In contrast, carbon would be called the excess reagent. There was more than enough of it to react with the other reactant(s).
Now, in the example problem, we were more or less told which reactant was the
limiting reagent. However, many times you will have to figure this out.
Problem: Salt (sodium chloride) is prepared by the reaction of sodium
metal with chlorine gas.
| 2Na(s) + Cl2(g)→2NaCl(s) |
You have 71.68 L of Cl2(g) and 6.7 moles of Na(s). What is the limiting reagent? How many moles of salt are produced?
Solution: Did you check to make sure the equation was balanced? It already is, but give yourself a congratulatory punch in the shoulder if you remembered (don't hurt yourself). Our next step, as always is to convert to moles.
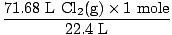 = 3.2 moles Cl2(g) = 3.2 moles Cl2(g) |
So now we know there is 3.2 moles of Cl2(g) and 6.7 moles of Na(s). Let's assume Na(s) is the limiting reagent and then prove our assumption right or wrong. How many moles of Na(s) are required to react completely with 3.2 moles of Cl2(g)? Use the mole ratio.
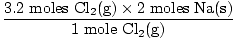 = 6.4 moles Na(s) = 6.4 moles Na(s) |
Do you have 6.4 moles of Na(s)? Yes, you do. You have 6.7 moles of Na(s). This is more than enough to react with all the Cl2(g). Our assumption was wrong, Na(s) is not the limiting reagent since there is more than enough of the solid. Since this reaction features only two reactants, we already know that Cl2(g) is the limiting reagent. Let's prove it.
 = 3.35 moles Cl2(g) = 3.35 moles Cl2(g) |
3.35 moles of Cl2(g) are needed to react completely with all the Na(s). You have only 3.2 moles. Cl2(g) is obviously the limiting reagent. Now let's figure out how many moles of salt (NaCL) are produced. We want to use the mole ratio from Cl2(g) since it has determined how many moles of each reactant will react.
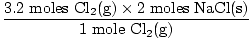 = 6.4 moles NaCl(s) = 6.4 moles NaCl(s) |


 payment page
payment page



