-
Aggregate Demand
The combined demand of all buyers in a market.
-
Budget Constraint
The outermost boundary of possible purchase combinations that a person can make, given how much money they have and the price of the goods in consideration.
-
Buyer
Someone who purchases goods and services from a seller for money.
-
Competition
In a market economy, competition occurs between large numbers of buyers and sellers who vie for the opportunity to buy or sell goods and services. The competition among buyers means that prices will never fall very low, and the competition among sellers means that prices will never rise very high. This is only true if there are so many buyers and sellers that no one individual has a significant impact on the market's equilibrium.
-
Complementary Good
A good is called a complementary good if the demand for the good increases with demand for another good. One extreme example: right shoes are complementary goods for left shoes.
-
Demand
Demand refers to the amount of goods and services that buyers are willing to purchase. Typically, demand decreases with increases in price, this trend can be graphically represented with a demand curve. Demand can be affected by changes in income, changes in price, and changes in relative price.
-
Demand Curve
A demand curve is the graphical representation of the relationship between quantities of goods and services that buyers are willing to purchase and the price of those goods and services. Example:
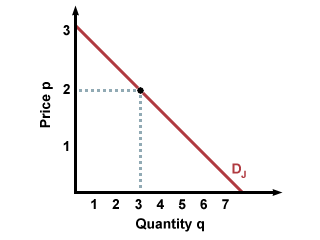
A Sample Demand Curve -
Diminishing Returns
Concept that the marginal utility derived from acquiring successive identical goods decreases with increasing quantities of goods.
-
Economics
Economics is the study of the production and distribution of scarce resources, and goods and services.
-
Equilibrium Price
The price of a good or service at which quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. Also called the market-clearing price.
-
Equilibrium Quantity
Amount of goods or services sold at the equilibrium price. Because supply is equal to demand at this point, there is no surplus or shortage.
-
Expected Value (EV)
How much a buyer thinks that a good or investment will be worth after a time lapse, based on the probabilities of different possible outcomes. Usually refers to stocks and other uncertain investments.
-
Giffen Good
Theoretical case in which an increase in the price of a good causes an increase in quantity demanded.
-
Firm
Unit of sellers in microeconomics. Because it is seen as one selling unit in microeconomics, a firm will make coordinated efforts to maximize its profit through sales of its goods and services. The combined actions and preferences of all firms in a market will determine the appearance and behavior of the supply curve.
-
Goods and Services
Products or work that are bought and sold. In a market economy, competition among buyers and sellers sets the market equilibrium, determining the price and the quantity sold.
-
Horizontal addition
The process of adding together all quantities demanded at each price level to find aggregate demand
-
Household
Unit of buyers in microeconomics. Because it is seen as one buying unit in microeconomics, a household will make coordinated efforts to maximize its utility through its choices of goods and services. The combined actions and preferences of all households in a market will determine the appearance and behavior of the demand curve.
-
Income Effect
Income effect describes the effects of changes in prices on consumption. According to the income effect, an increase in price causes a buyer to feel poorer, lowering the quantity demanded, and vice versa. Although the buyer's actual income hasn't changed, the change in price makes the buyer feel as if it has.
-
Indifference Curve
Graphical representation of different combinations of goods and services that give a consumer equal utility or happiness.
-
Inferior Good
A good for which quantity demanded decreases with increases in income.
-
Marginal Utility
Additional utility derived from each additional unit of goods acquired.
-
Market
A large group of buyers and sellers who are buying and selling the same good or service.
-
Market Economy
An economy in which the prices and distribution of goods and services are determined by the interaction of large numbers of buyers and sellers who have no significant individual impact on prices or quantities.
-
Market-clearing Price
The price of a good or service at which quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. Also called the equilibrium price.
-
Microeconomics
Subfield of economics which studies how households and firms behave and interact in the market.
-
Normal Good
A normal good is a good for which an increase in income causes an increase in demand, and vice versa.
-
Optimization
To maximize utility by making the most effective use of available resources, whether they be money, goods, or other factors.
-
Resource
A supply of capital that can be used in an economy. Because resources are scarce, however, there is not enough to go around.
-
Risk
Refers to the amount of variation in possible payoffs. A very risky investment will have wide variation in possible payoffs, but might have a higher expected value; a less risky investment will have a more predictable payoff, but a lower expected value.
-
Risk-averse
Refers to a buyer who is unwilling to invest in an investment with wide variation in possible payoffs. Someone who is risk-averse might even refuse to invest in something with a positive expected value if the variation in possible outcomes is too great.
-
Risk-loving
Refers to a buyer who is willing to invest in an investment with wide variation in possible payoffs, in the hopes of getting a large return. In extreme cases, a risk lover might even invest in something with a negative expected value.
-
Risk-neutral
Refers to a buyer who does not care about variation in possible payoffs. A risk-neutral buyer will invest in any investment with a positive expected return, regardless of how risky it is.
-
Scarcity
Goods, services, or resources are scarce if there is not enough for everyone to have as much as they would like.
-
Seller
Someone who sells goods and services to a buyer for money.
-
Substitute Good
Refers to a good which is to some extent interchangeable with another good, meaning that when the price of one good increases, demand for the other good increases.
-
Substitution Effect
Describes the effects of changes in relative prices on consumption. According to the substitution effect, an increase in price of one good causes a buyer to buy more of the other good, since the first good has become relatively expensive, and vice versa. The buyer substitutes consumption of the second good for consumption of the first.
-
Supply
Supply refers to the amount of goods and services that sellers are willing to sell. Typically, supply increases with increases in price, this trend can be graphically represented with a supply curve.
-
Utility
An approximate measure for levels of "happiness."
-
Wage
Price per unit of time when the good being sold is some form of labor or work (as opposed to a physical product).













