-
Asymptote
A line that a function approaches but never intersects.
-
Axis
The line of symmetry of a parabola.
-
Constant Function
A polynomial function of degree zero in which the constant term ≠ 0.
-
Constant Term
The coefficient of x0 in a polynomial.
-
Degree
The value of n in a polynomial f (x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a1x + a0, where an≠ 0. If f (x) = 0, then the degree is undefined.
-
Descartes' Rule of Signs
Descartes' Rule of Signs states that the number of positive real roots is less than or equal to the number of variations in the function f (x). It also states that the number of negative real roots is less than or equal to the number of variations in the function f (- x).
-
Leading Coefficient
The value of an in a polynomial f (x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a1x + a0, where an≠ 0 unless f (x) = 0.
-
Linear Function
A first-degree polynomial.
-
Multiplicity
If (x - c)n is a factor of a polynomial but (x - c)n+1 is not, the root c is said to be a root of multiplicity n.
-
Parabola
Another name for the graph of a quadratic function.
-
Polynomial
An expression of one variable of the form anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a2x2 + a1x + a0, where an, an-1,..., a1, a0 are real numbers, n is a nonnegative integer, and an≠ 0.
-
Polynomial Function
A function that is defined by a polynomial; it is of the form f (x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a2x2 + a1x + a0, where an, an-1,…, a1, a0 are real numbers, n is a nonnegative integer, and an≠ 0.
-
Quadratic Function
A second-degree polynomial.
-
Rational Function
A function which can be expressed as the quotient of two polynomial functions.
-
Rational Root Theorem
The Rational Root Theorem is a useful tool in finding the roots of a polynomial function f (x) = anxn + an-1xn-1 + ... + a2x2 + a1x + a0. If the coefficients of a polynomial are all integers, and a root of the polynomial is rational (it can be expressed as a fraction in lowest terms), the Rational Root Theorem states that the numerator of the root is a factor of a0 and the denominator of the root is a factor of an.
-
Root
Values of the independent variable for which a polynomial function equals zero.
-
Variation
Consecutive terms of a polynomial whose coefficients have opposite signs.
-
Vertex
The point on a parabola at which the quadratic function reaches its minimum or maximum value.
-
Zero Polynomial
The polynomial f (x) = 0.
Terms
Formulae
| Quadratic Formula |
If ax2 + bx + c = 0, then x = 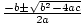 . .
|













